PMML模型文件在机器学习的实践经验 - CSDN博客
算法工程师和业务开发工程师,所掌握的技能容易在长期的工作中出现比较深的鸿沟,算法工程师辛辛苦苦调参的成果,业务工程师可能不清楚如何使用,如何为线上决策给予支持。本文介绍一种基于PMML的模型上线方法。
这种方案,在本次参加 QCon 大会时,Paypal的机器学习平台中也有所提及:
PMML
预测模型标记语言(Predictive Model Markup Language,PMML)是一种可以呈现预测分析模型的事实标准语言。标准东西的好处就是,各种开发语言都可以使用相应的包,把模型文件转成这种中间格式,而另外一种开发语言,可以使用相应的包导入该文件做线上预测。
不过,当训练和预测使用同一种开发语言的时候,PMML 就没有必要使用了,因为任何中间格式都会牺牲掉独有的优化。本文介绍的内容是采用Python语言做模型训练,线上采用 Java 载入模型做预测。在模型训练端,分别介绍了 python sk-learn 和 xgboost 训练模型。
正式开始之前,首先总结下模型训练和线上预测的流程图
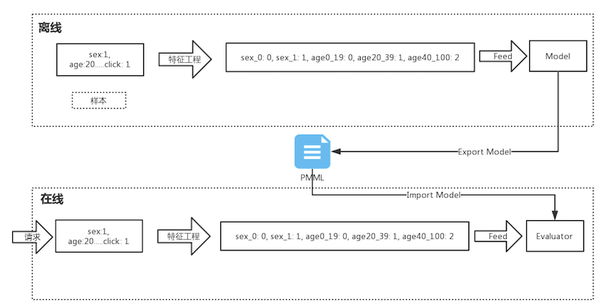
离线部分负责模型训练和导出模型,线上导入模型并且做预测。当然特征工程部分主要做特征变换,例如 分桶,单值编码,归一化等。
SK-Learn
该开源项目支持 sk-learn模型转成PMML,项目地址: jpmml/sklearn2pmml,扩充了一个例子定义如何使用sk-learn导出带有特征工程的模型文件
heart_data=pandas.read_csv("heart.csv")#用Mapper定义特征工程mapper=DataFrameMapper([(['sbp'],MinMaxScaler()),(['tobacco'],MinMaxScaler()),('ldl',None),('adiposity',None),(['famhist'],LabelBinarizer()),('typea',None),('obesity',None),('alcohol',None),(['age'],FunctionTransformer(np.log)),])#用pipeline定义使用的模型,特征工程等pipeline=PMMLPipeline([('mapper',mapper),("classifier",linear_model.LinearRegression())])pipeline.fit(heart_data[heart_data.columns.difference(["chd"])],heart_data["chd"])#导出模型文件sklearn2pmml(pipeline,"lrHeart.xml",with_repr=True)heart.csv定义结构如下:
sbp,tobacco,ldl,adiposity,famhist,typea,obesity,alcohol,age,chd
160,12,5.73,23.11,Present,49,25.3,97.2,52,1
144,0.01,4.41,28.61,Absent,55,28.87,2.06,63,1
118,0.08,3.48,32.28,Present,52,29.14,3.81,46,0
170,7.5,6.41,38.03,Present,51,31.99,24.26,58,1
134,13.6,3.5,27.78,Present,60,25.99,57.34,49,1
132,6.2,6.47,36.21,Present,62,30.77,14.14,45,0
142,4.05,3.38,16.2,Absent,59,20.81,2.62,38,0
114,4.08,4.59,14.6,Present,62,23.11,6.72,58,1
114,0,3.83,19.4,Present,49,24.86,2.49,29,0
132,0,5.8,30.96,Present,69,30.11,0,53,1
206,6,2.95,32.27,Absent,72,26.81,56.06,60,1
134,14.1,4.44,22.39,Present,65,23.09,0,40,1
模型文件导出后,可以把文件存储在公司内部文件存储,实在不行可以打包在 jar 包中,供线上调用。
Java端采用 jpmml/jpmml-evaluator项目,载入 PMML 文件,然后准备线上所需数据,示例代码如下:
//准备画像数据-key和原始特征一致即可
lrHeartInputMap.put("sbp", 142);
lrHeartInputMap.put("tobacco", 2);
lrHeartInputMap.put("ldl", 3);
lrHeartInputMap.put("adiposity", 30);
lrHeartInputMap.put("famhist", "Present");
lrHeartInputMap.put("typea", 83);
lrHeartInputMap.put("obesity", 23);
lrHeartInputMap.put("alcohol", 90);
lrHeartInputMap.put("age", 30);
//预测核心代码
public static void predictLrHeart() throws Exception {
PMML pmml;
//模型导入
File file = new File("lrHeart.xml");
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
try (InputStream is = inputStream) {
pmml = org.jpmml.model.PMMLUtil.unmarshal(is);
ModelEvaluatorFactory modelEvaluatorFactory = ModelEvaluatorFactory.newInstance();
ModelEvaluator<?> modelEvaluator = modelEvaluatorFactory.newModelEvaluator(pmml);
Evaluator evaluator = (Evaluator) modelEvaluator;
List<InputField> inputFields = evaluator.getInputFields();
//过模型的原始特征,从画像中获取数据,作为模型输入
Map<FieldName, FieldValue> arguments = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (InputField inputField : inputFields) {
FieldName inputFieldName = inputField.getName();
Object rawValue = lrHeartInputMap.get(inputFieldName.getValue());
FieldValue inputFieldValue = inputField.prepare(rawValue);
arguments.put(inputFieldName, inputFieldValue);
}
Map<FieldName, ?> results = evaluator.evaluate(arguments);
List<TargetField> targetFields = evaluator.getTargetFields();
//获得结果,作为回归预测的例子,只有一个输出。对于分类问题等有多个输出。
for (TargetField targetField : targetFields) {
FieldName targetFieldName = targetField.getName();
Object targetFieldValue = results.get(targetFieldName);
System.out.println("target: " + targetFieldName.getValue() + " value: " + targetFieldValue);
}
}
}特征工程的说明
如流程图所示,对于原始样本数据,首先要做特征工程输入算法需要数据。特征工程可以线上线下,分开单独做,也可以用 DataFrameMapper 的方式实现特征工程,导出到模型文件中,这样线上就不需要再实现一次特征工程,但缺点是只可以使用Sklearn包中提供的方法,自拓展的方法无法支持(例如 Bucketizer)
支持的特征工程方法
- preprocessing.Binarizer #二值化,例如大于 5 变成 1,小于等于 5 变成 0
- preprocessing.FunctionTransformer # 支持 np 包中,简单的一些函数,例如 np.log.
- preprocessing.Imputer
- preprocessing.LabelBinarizer # 对于string类型的,one-hot
- preprocessing.LabelEncoder
- preprocessing.MaxAbsScaler
- preprocessing.MinMaxScaler # min max 归一
- preprocessing.OneHotEncoder # 对于数值的 one-hot
- preprocessing.PolynomialFeatures #把两个特征,拆成多个N次组合特征,例如x,y 变成 x y x^2 y^2 xy
- preprocessing.RobustScaler
- preprocessing.StandardScaler
Sklearn preprocessing 暂时不支持 分桶,该操作不久会被支持,已经有开源贡献者提交了 Merge Request,在Sk支持后,相信不久 JPMML项目也会支持
https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn/pull/9342
XGBoost
模型原理的理解可以参考这篇文章: GBDT的原理和应用
XGBoost 输入的文件格式是 SVMLib 文件格式。
1 3:1 10:1 11:1 21:1 30:1 34:1 36:1 40:1 41:1 53:1 58:1 65:1 69:1 77:1 86:1 88:1 92:1 95:1 102:1 105:1 117:1 124:1
0 3:1 10:1 20:1 21:1 23:1 34:1 36:1 39:1 41:1 53:1 56:1 65:1 69:1 77:1 86:1 88:1 92:1 95:1 102:1 106:1 116:1 120:1
0 1:1 10:1 19:1 21:1 24:1 34:1 36:1 39:1 42:1 53:1 56:1 65:1 69:1 77:1 86:1 88:1 92:1 95:1 102:1 106:1 116:1 122:1
1 3:1 9:1 19:1 21:1 30:1 34:1 36:1 40:1 42:1 53:1 58:1 65:1 69:1 77:1 86:1 88:1 92:1 95:1 102:1 105:1 117:1 124:1
第一列是 label,后面的是特征Id对应的值。和他一起使用的,有个特征文件,定义了特征工程方法。
0 cap-shape=bell i
1 cap-shape=conical i
2 cap-shape=convex i
3 cap-shape=flat i
4 cap-shape=knobbed i
i: indicator, 二值特征
q: quantitative, 数值特征,例如年龄等
int: int means this feature is integer value (when int is hinted, the decision boundary will be integer)
模型训练完毕后,导出模型文件 (.model) 。使用 jpmml/jpmml-xgboost 转模型文件成PMML格式。 可以和feature map文件作为输入,这样线上就不需要重新定义特征工程。
示例命令如下: java -jar target/converter-executable-1.2-SNAPSHOT.jar --model-input 0002.model --fmap-input featmap.txt --target-name mpg --pmml-output xgboost.pmml
线上使用的方法和前例基本一致,准备好原始特征值,过模型即可
xgBoostInputMap.put("mpg","1");
xgBoostInputMap.put("bruises?", "no");
xgBoostInputMap.put("odor", "creosote");
xgBoostInputMap.put("gill-spacing", "close");
xgBoostInputMap.put("gill-size", "narrow");
xgBoostInputMap.put("stalk-root", "club");
xgBoostInputMap.put("stalk-surface-below-ring", "smooth");
xgBoostInputMap.put("spore-print-color", "orange");总结
因为PMML格式的通用性,所以会丧失特殊模型的特殊优化,例如上线XGBoost模型,也可以使用XGBoost4J,该包会链接一个本地环境编译的 .so 文件,C++实现的核心代码效率很高。不过PMML格式通用,在效率要求不高的场景可以发挥很大作用。
对于特征工程部分的计算,PMML对特征工程对支持有限,线上、线下可以单独实现,PMML文件只负责模型部分,这样既可以做丰富的特征工程,也实现了模型的共用。
传送门:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/30378213