Elasticsearch:rollup - 索引管理_Elastic-CSDN博客_elasticsearch rollup
汇总作业 ( rollup jobs)是一项定期任务,它将来自索引模式指定的索引中的数据进行汇总,然后将其汇总到新的索引中。 汇总索引是紧凑存储数月或数年历史数据以供可视化和报告使用的好方法。用到rollup的情况是我们有很多的历史数据,而且通常会比较大。通过使用 rollup 功能,我们可以把很多针对大量数据的统计变为针对经过 rollup 后的索引操作,从而使得数据的统计更加有效。在实际的应用中:
- 在很多的情况下,保留历史数据不是一种最佳的选择。这是因为时序数据随着时间的推移,它们的价值没有那么高,需要删除这些数据以节省成本
- 但是我们还是希望能够保留它们的统计数据用于分析
Elasticsearch 自6.3 版本推出 rollup功能,它可以帮我们:
- 保留旧数据,并以一种紧凑和聚合的方式来存储
- 仅仅保留我们感兴趣的数据
在下面,我们来用一个具体的例子来展示如何使用rollup的。
准备数据
我们首先需要找到一个数据比较大一点的索引。我们可以参考我之前的文章 “ Logstash 入门教程 (二)” 。在那篇文章中,我们直接跳到文章的最后一节把整个文件都导入到Elasticticsearch中。
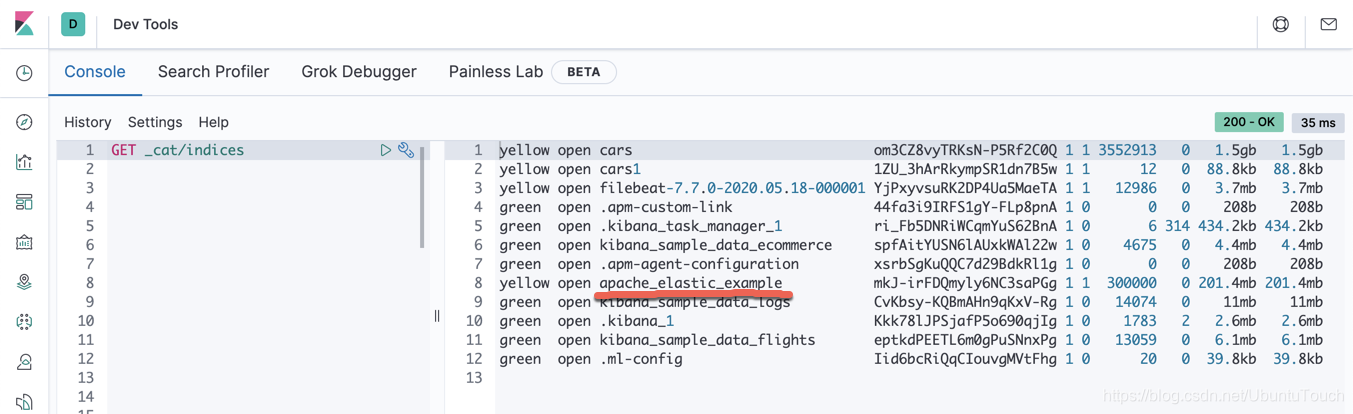
我们可以看到我们的cars索引有达到201M的大小,而且它的总文档数达到 30 万。在接下来我们将使用 rollup 的功能对这个索引进行处理。在数据导入后,我们必须创建一个index pattern,并在Discover中进行显示:
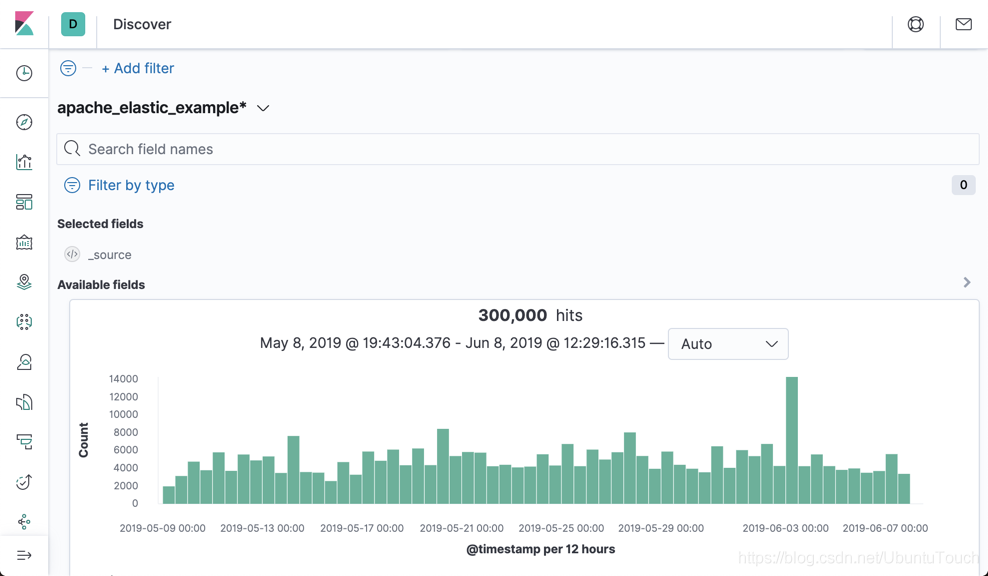
从上面的图中,我们可以看出来,整个索引的数据是从2019.5.9到2019.6.07进行采集的。
创建 rollup job
我们打开 Kibana 界面:
点击 Create rollup job按钮:
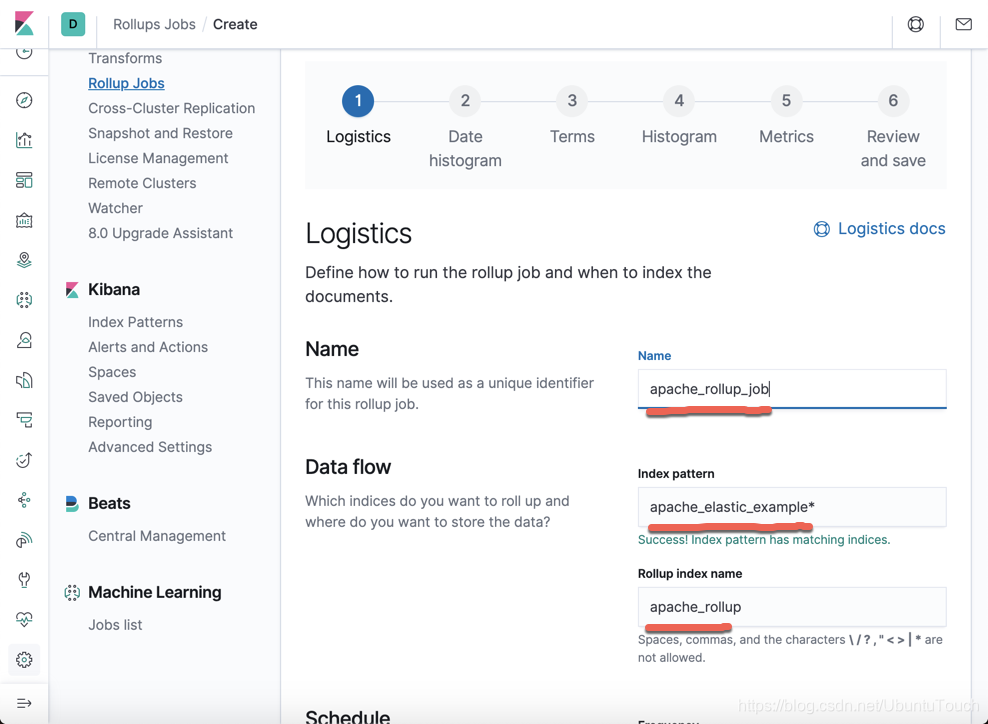
从上面我们可以看出来这个 rollup job 针对一个时间系列的索引。把屏幕向下滚动。
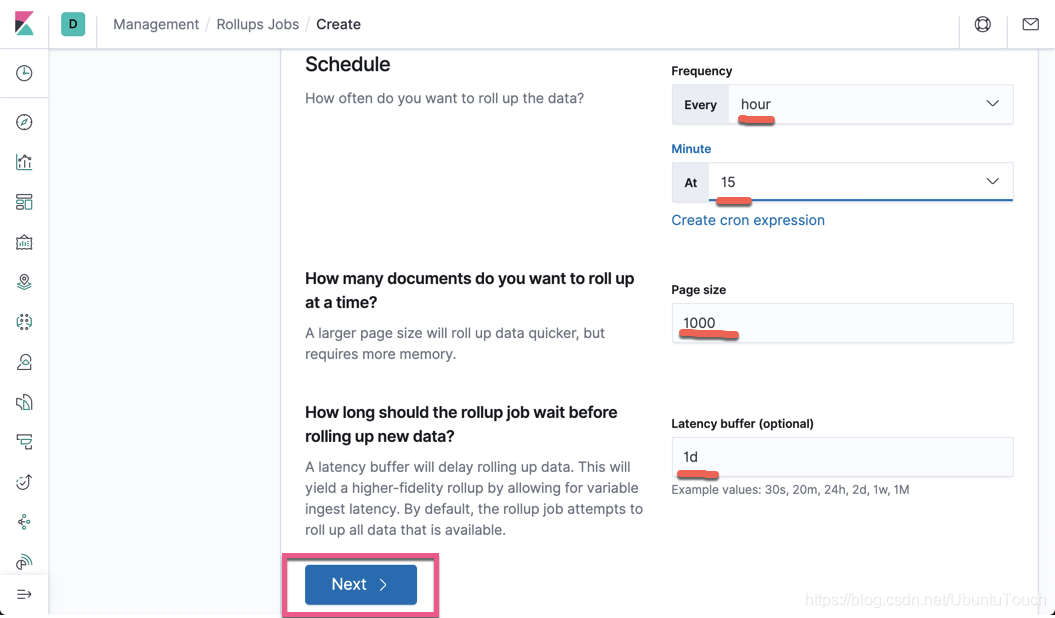
从上面我们可以看出来:rollup 是一个在后台不断运行的一个任务。它会周期性地定时做这项工作,以使得最新已有的数据得到处理。在上面,我选择在每个时钟过15分钟时进行一次rollup,比如在1:15分做一次,2:15分做一次,3:15分做一次,依次类推。这个依赖于你自己索引的大小及项目的性质决定的。
点击上面的 Next 按钮:
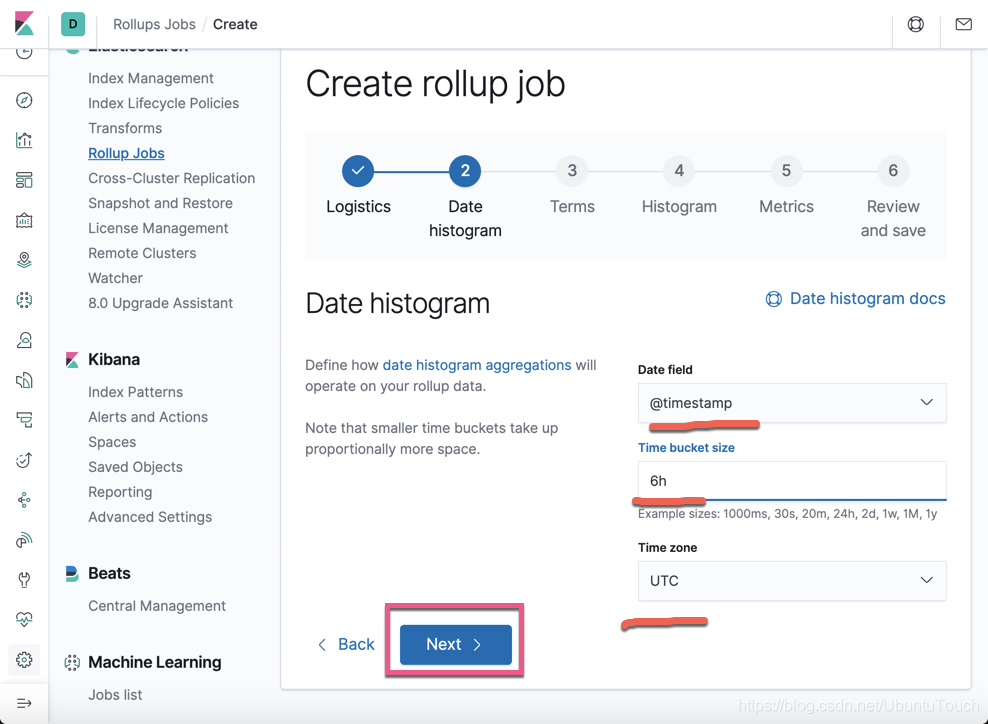
这个是针对 Date histogram 的配置。点击 Next 按钮:
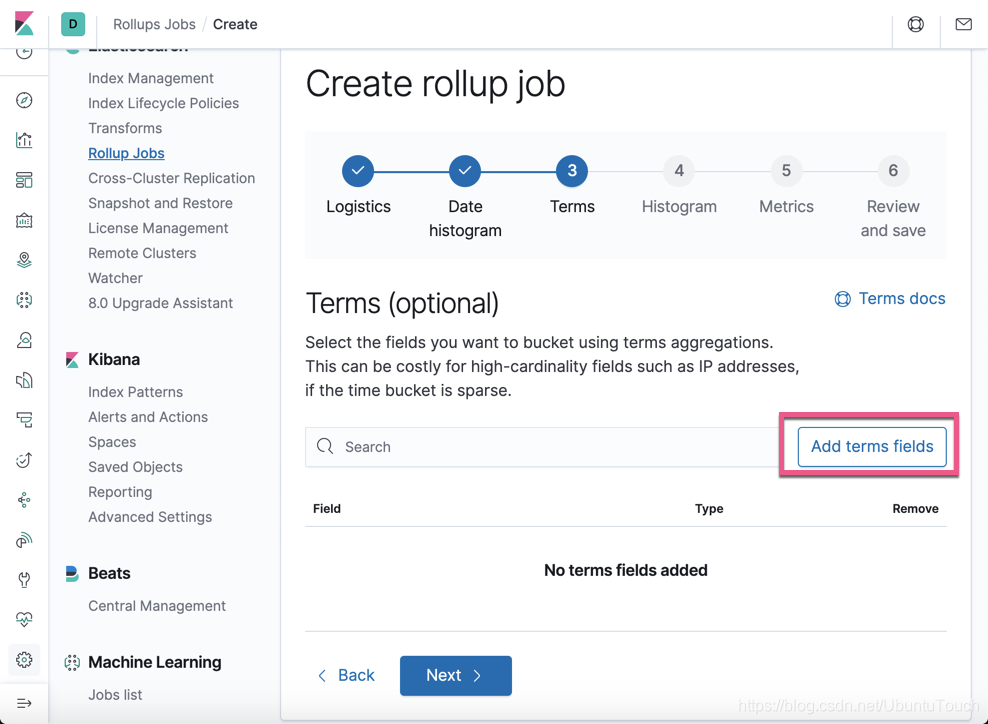
这个是针对 terms 的 选择。点击 Add terms fields 按钮:
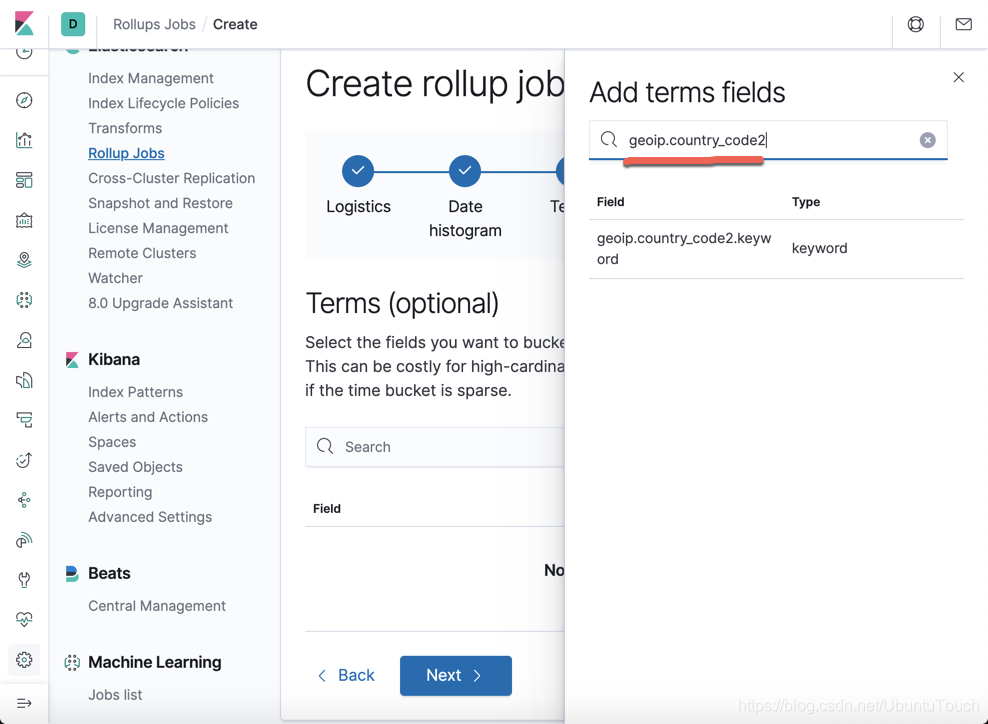
我们选择上面的 geoip.country_code2:
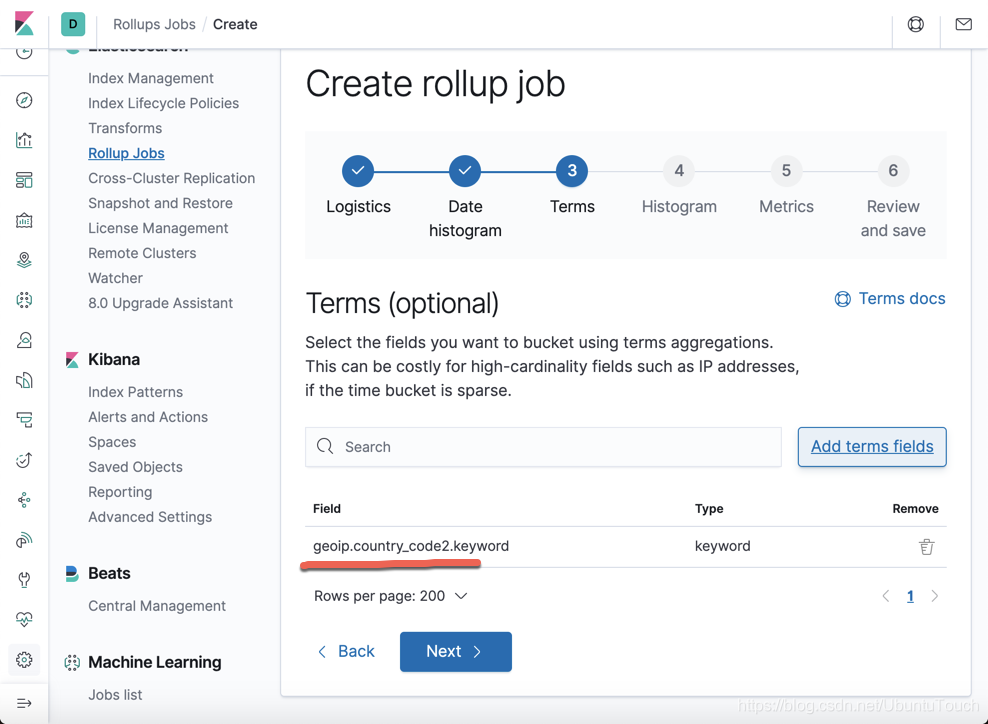
按照同样的方法,我们添加 agent.hostname:
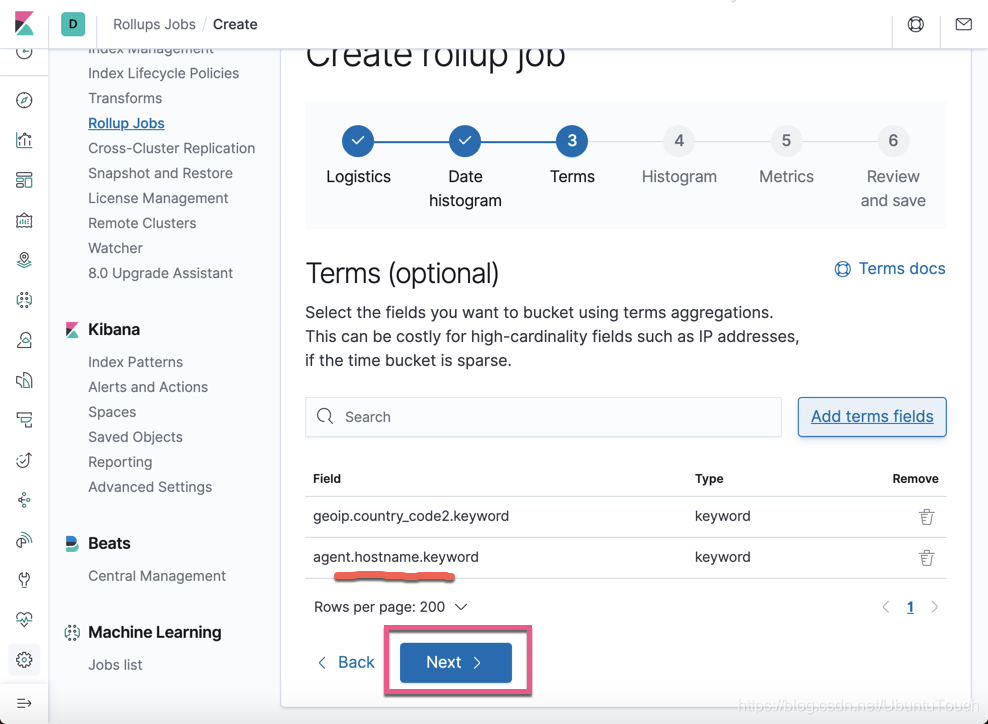
点击 Next 按钮:
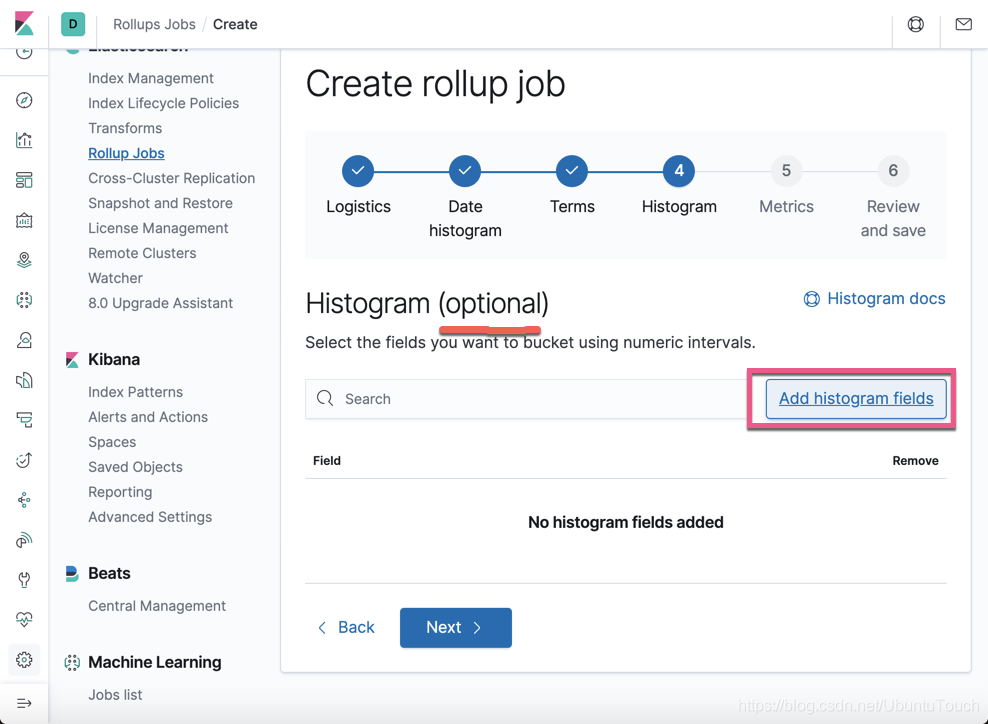
这个页面时可选项。如果我们感兴趣的话,那么我们点击 Add histogram fields:
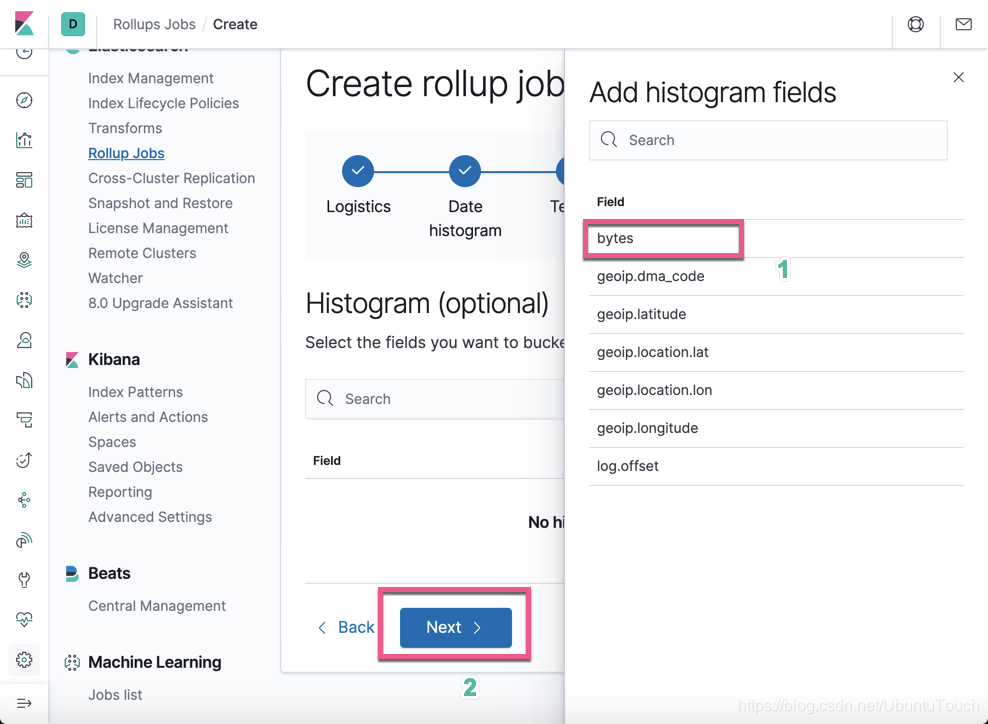
我们选择 Bytes 字段:
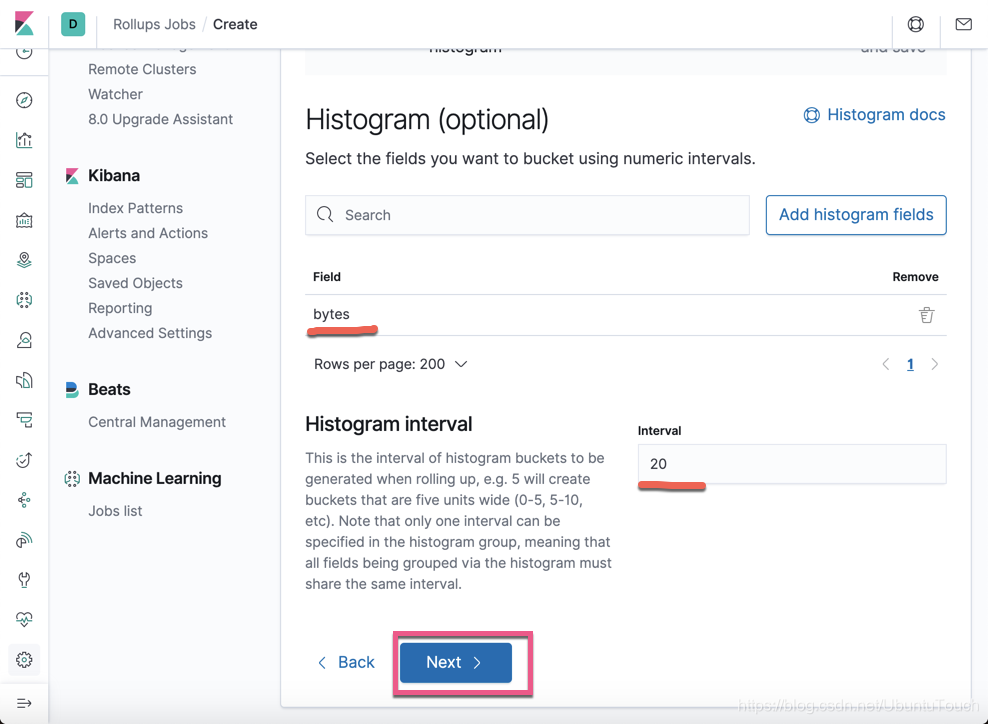
点击 Next 按钮:
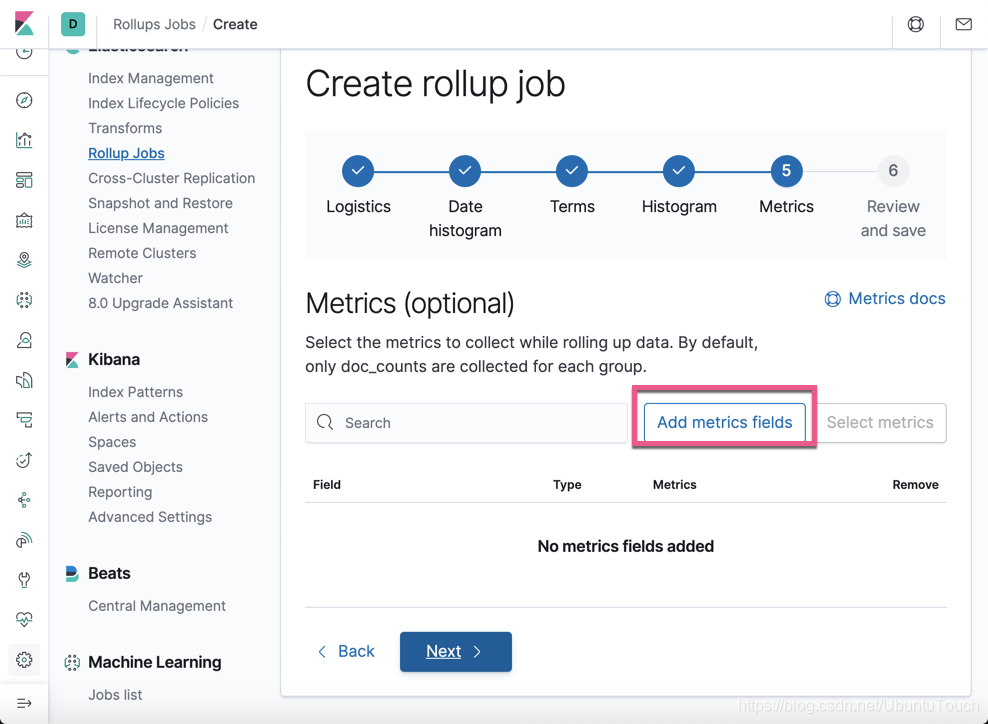
这个是对 Metrics 的配置。我们点击 Add metrics fields按钮:
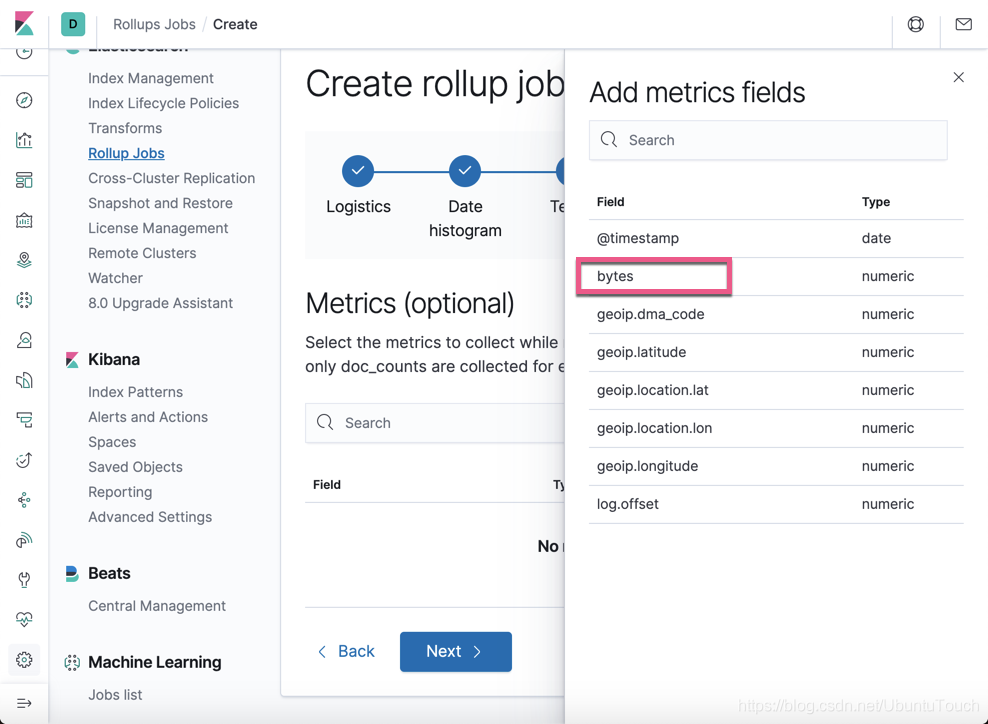
我们选择 bytes。由于 Metrics 只是针对数值类型的字段,在上面我们可以看到所有的字段都是数值类型的。
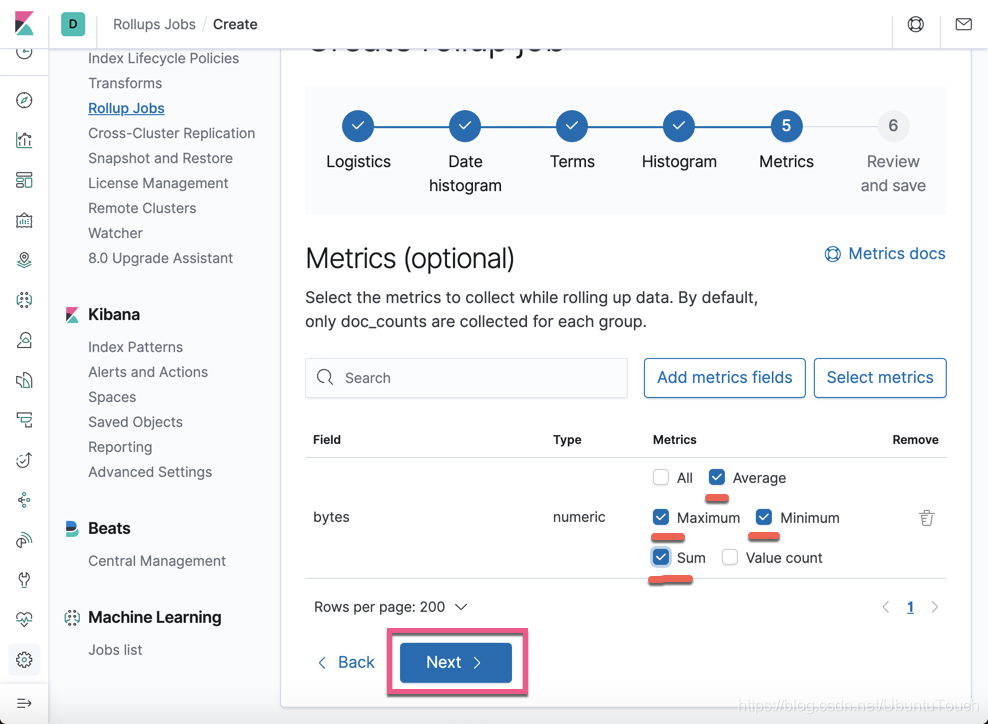
我们接着勾上我们喜欢的 metrics 项。再点击 Next 按钮:
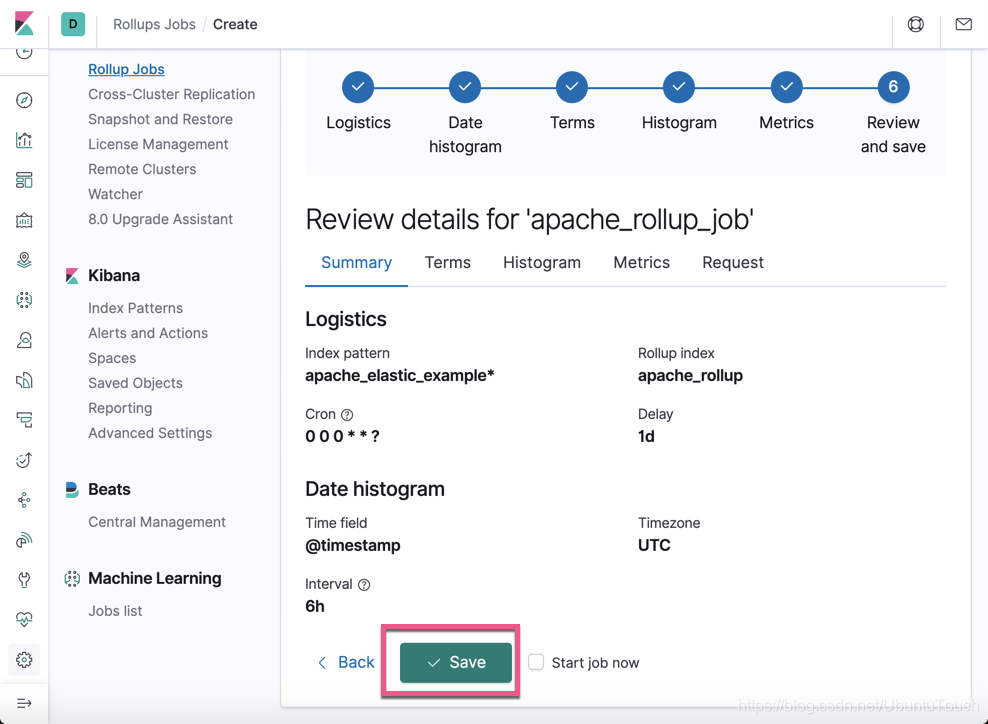
在这个页面我们可以看到这个 rollup 的 概览。如果你觉得不太满意,你可以点击 Back 按钮然后再进行重新配置。如果满意的话,我们点击 Save 按钮。如果你还想马上就开始这个 job 的话,勾上 Start job now。我们点击 Save,并勾上 Start job now:
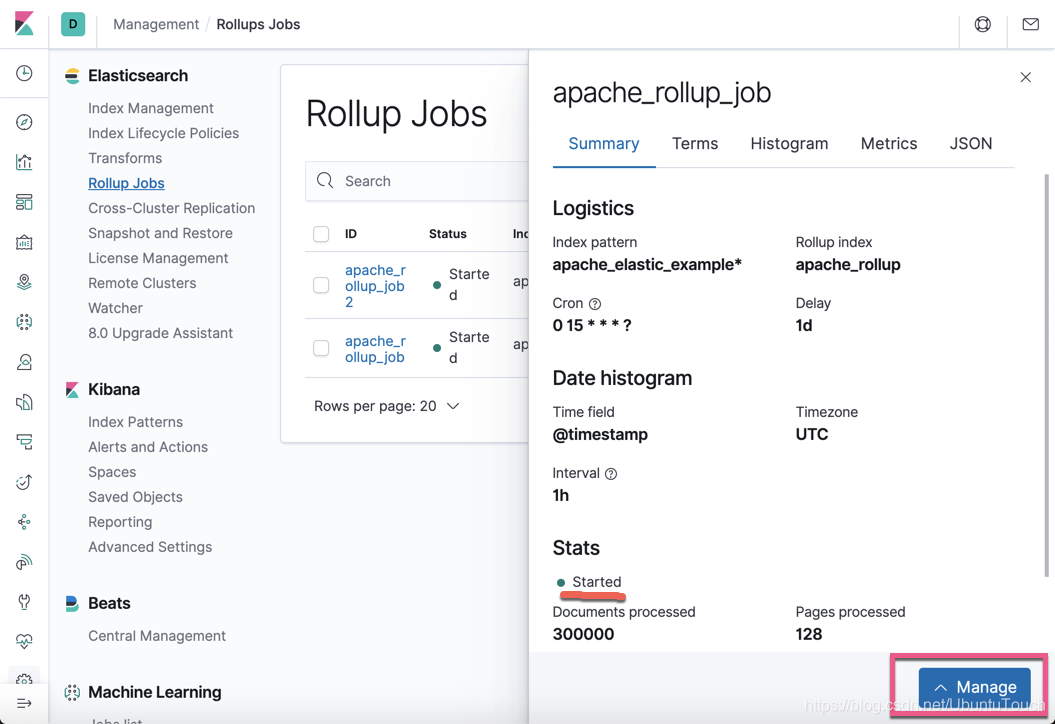
上面的状态显示这个job已经开始工作了。我们可以点击 Manage 按钮来对这个 job 进行管理:
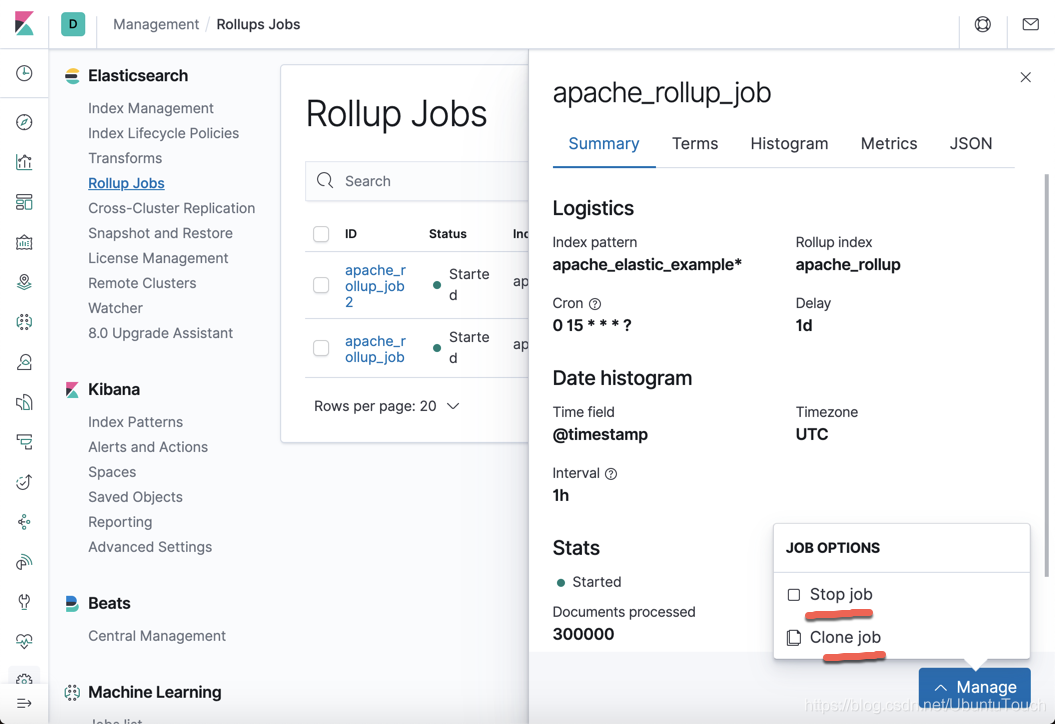
它可以让我们停止这个 job 或者 克隆这个job。目前,我们既不想停止,也不想克隆。我们在这个界面还可以点击上面的几个tab来查看这个job的详细信息。
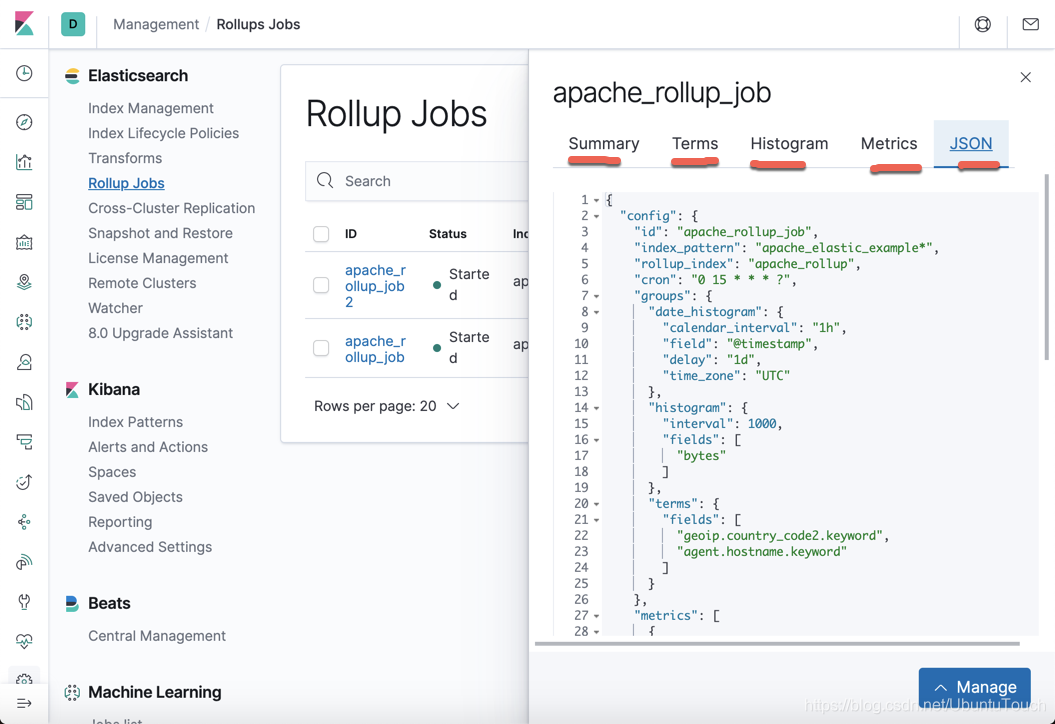
特别有意思的是我们甚至可以看到这个 job 的JSON 表达方式。
退出这个Dialog:
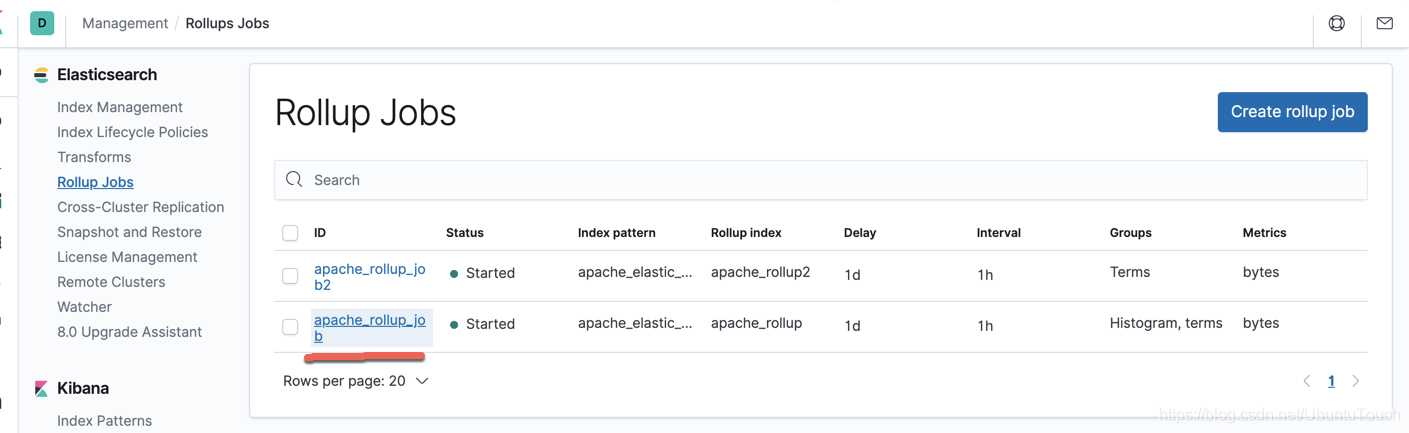
从上面,我们可以看出来我们的 Job 正在运行中。
在 Kibana 中进行统计
我在Kibana中,通过如下的命令来查看所有的索引:
GET _cat/indices 结果显示:
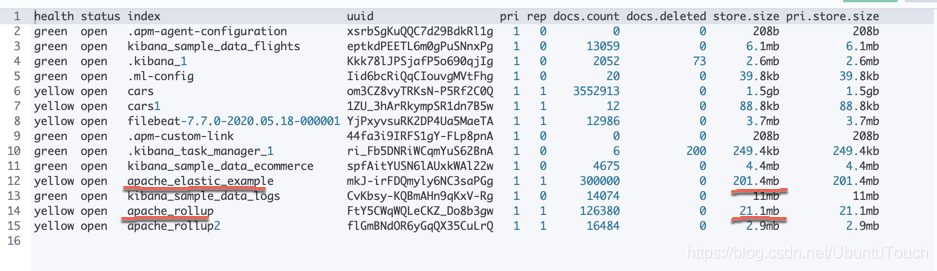
我们可以看到一个新的索引:apache_rollup。它的文件显示的非常之小。只有21.8M。是不是觉得不可思议啊。它相比之前的那个apache_elastic_example 来说,小了非常多。
我们通过对这个索引来对我们所关心的数据进行统计分析。当我们对这个 rollup 的索引进行分析时,参照链接 https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/master/rollup-search.html,我们可以对它进行如下的方式的搜索:
我们经过 rollup 的处理后,那么对于我们的数据的统计来说有没有什么影响呢?
我们先来做一些检测:
找出最大值
GET apache_rollup/_rollup_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"my_max": {
"max": {
"field": "bytes"
}
}
}
} 返回结果:
{
"took" : 9,
"timed_out" : false,
"terminated_early" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my_max" : {
"value" : 8.2090432E7
}
}
} 上面是根据 rollup 的索引得到的结果。我们来使用最原始的索引:
GET apache_elastic_example/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"my_max": {
"max": {
"field": "bytes"
}
}
}
} {
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 10000,
"relation" : "gte"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my_max" : {
"value" : 8.209043E7
}
}
} 显然返回的结果是一样的。
找出最小值
GET apache_rollup/_rollup_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"my_min": {
"min": {
"field": "bytes"
}
}
}
} 返回的结果:
{
"took" : 7,
"timed_out" : false,
"terminated_early" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my_min" : {
"value" : 1.0
}
}
} 使用原始的数据:
GET apache_elastic_example/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"my_min": {
"min": {
"field": "bytes"
}
}
}
} {
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 10000,
"relation" : "gte"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my_min" : {
"value" : 1.0
}
}
} 返回的结果是一样的。
找出平均值
GET apache_rollup/_rollup_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"my_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "bytes"
}
}
}
} {
"took" : 13,
"timed_out" : false,
"terminated_early" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my_avg" : {
"value" : 2372996.9378802367
}
}
} 使用原始的数据:
GET apache_elastic_example/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"my_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "bytes"
}
}
}
} 返回的结果是:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 10000,
"relation" : "gte"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my_avg" : {
"value" : 2372996.957136324
}
}
} 结果的差异是非常之小的。
找出文档最多的前5个国家的名称
GET apache_rollup/_rollup_search
{
"size":0,
"aggs" : {
"countries": {
"terms": {
"field": "geoip.country_code2.keyword",
"size": 5
}
}
}
} "aggregations" : {
"countries" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 66600,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "US",
"doc_count" : 122800
},
{
"key" : "FR",
"doc_count" : 19226
},
{
"key" : "DE",
"doc_count" : 17415
},
{
"key" : "NL",
"doc_count" : 14720
},
{
"key" : "CN",
"doc_count" : 14581
}
]
}
} 使用最原始的数据:
GET apache_elastic_example/_search
{
"size":0,
"aggs" : {
"countries": {
"terms": {
"field": "geoip.country_code2.keyword",
"size": 5
}
}
}
} "aggregations" : {
"countries" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 109662,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "US",
"doc_count" : 122800
},
{
"key" : "FR",
"doc_count" : 19226
},
{
"key" : "DE",
"doc_count" : 17415
},
{
"key" : "NL",
"doc_count" : 14720
},
{
"key" : "CN",
"doc_count" : 14581
}
]
}
} 这两个的统计结果是一样的。
更为复杂的统计
我们可以尝试一下的统计:
GET apache_rollup/_rollup_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"term": {
"agent.hostname.keyword" : {
"value": "liuxg"
}
}
},
"aggs" :{
"daily" : {
"date_histogram" :{
"field": "@timestamp",
"calendar_interval": "1d",
"time_zone": "UTC"
},
"aggs": {
"avg_byete" : {
"avg": {
"field": "bytes"
}
}
}
}
}
} 上面是对 rollup 索引进行的统计:
"aggregations" : {
"daily" : {
"meta" : { },
"buckets" : [
{
"key_as_string" : "2019-05-08T00:00:00.000Z",
"key" : 1557273600000,
"doc_count" : 688,
"avg_byete" : {
"value" : 126608.41791044777
}
},
{
"key_as_string" : "2019-05-09T00:00:00.000Z",
"key" : 1557360000000,
"doc_count" : 7721,
"avg_byete" : {
"value" : 317026.4027212793
}
},
{
"key_as_string" : "2019-05-10T00:00:00.000Z",
"key" : 1557446400000,
"doc_count" : 9044,
"avg_byete" : {
"value" : 551951.1379390019
}
},
{
"key_as_string" : "2019-05-11T00:00:00.000Z",
"key" : 1557532800000,
"doc_count" : 9412,
"avg_byete" : {
"value" : 261766.84161836826
}
},
...
} 我们对最原始的索引来进行统计:
GET apache_elastic_example/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"term": {
"agent.hostname.keyword": {
"value": "liuxg"
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"daily": {
"date_histogram": {
"field": "@timestamp",
"calendar_interval": "1d",
"time_zone": "UTC"
},
"aggs": {
"avg_bytes": {
"avg": {
"field": "bytes"
}
}
}
}
}
} 显示结果:
"aggregations" : {
"daily" : {
"buckets" : [
{
"key_as_string" : "2019-05-08T00:00:00.000Z",
"key" : 1557273600000,
"doc_count" : 688,
"avg_bytes" : {
"value" : 126608.41940298508
}
},
{
"key_as_string" : "2019-05-09T00:00:00.000Z",
"key" : 1557360000000,
"doc_count" : 7721,
"avg_bytes" : {
"value" : 317026.4042642727
}
},
{
"key_as_string" : "2019-05-10T00:00:00.000Z",
"key" : 1557446400000,
"doc_count" : 9044,
"avg_bytes" : {
"value" : 551951.1417513863
}
},
{
"key_as_string" : "2019-05-11T00:00:00.000Z",
"key" : 1557532800000,
"doc_count" : 9412,
"avg_bytes" : {
"value" : 261766.84351315204
}
},
...
} 从上面的结果显示,通过这两种方式进行的统计的结果非常一致。
从某种程度上讲,我们甚至可以通过Index cycle management的方法只保留一段时间的数据(比如最近的6个月的数据),而通过rollup 方法继续可以对之前的数据进行预设的统计。
通过 API 的方法实现
上面的方法通过界面非常直观。但是Elastic也提供API的方法来设置。比如:
PUT _rollup/job/apache_rollup_job2
{
"index_pattern": "apache_elastic_example*",
"rollup_index": "apache_rollup2",
"cron": "*/10 * * * * ?",
"page_size": 1000,
"groups": {
"date_histogram": {
"field": "@timestamp",
"fixed_interval": "1h",
"delay": "1d",
"time_zone": "UTC"
},
"terms": {
"fields": [
"geoip.country_code2.keyword",
"agent.hostname.keyword"
]
}
},
"metrics": [
{
"field": "bytes",
"metrics": [
"min",
"max",
"sum",
"avg"
]
}
]
} 在上面,我们设置了几乎和界面一样的实现,只不过在这里,我们每隔10分钟来进行一次 rollup。在这里,我们把数据存于到 apache_rollup2 这个索引中。
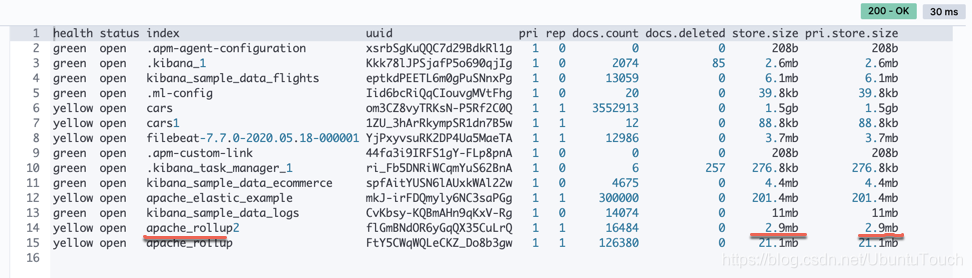
这个apache_rollup2 的大小更小。但是它和apache_rollup 是一样的效果。我们可以对这个索引做同样的搜索:
GET apache_rollup2/_rollup_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"my_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "bytes"
}
}
}
} "took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"terminated_early" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my_avg" : {
"value" : 2372996.9558440386
}
}
} 使用最原始的索引:
GET apache_elastic_example/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"my_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "bytes"
}
}
}
} {
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 10000,
"relation" : "gte"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my_avg" : {
"value" : 2372996.957136324
}
}
} 关于其它的比较,我这里就不详述了。你们可以自己来实践。
如果我们想删除一个 rollup 的任务,我们必须先停止,然后,删除它的 rollup 索引,再进行删除的动作。这些有的可以在之前的那个UI里通过 Manage 按钮来实现。通过 API的方式来删除一个 rollup,请参考如下的步骤:
POST _rollup/job/apache_rollup_job/_stop?wait_for_completion=true&timeout=10s
DELETE apache_rollup
DELETE _rollup/job/apache_rollup_job
参考:
【1】 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I5-9x_pQ-Y0&t=302s&pbjreload=10
【2】 https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/rollup-get-job.html
【3】 https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/master/rollup-search.html