hadoop实现单表和多表关联
转载请注明: http://hanlaiming.freetzi.com/?p=123
在mapreduce上编写简单应用后,开始学习稍微高级一点的单表关联和多表关联。
在学习过程中我参考了这篇文章,谢谢 http://www.cnblogs.com/xia520pi/archive/2012/06/04/2534533.html,里面很多基本的内容很实用。
一、单表关联。
实例中给出 child-parent(孩子——父母)表,要求输出 grandchild-grandparent(孙子——爷奶)表。
样例 输入如下所示。
- file:child parent
- Tom Lucy
- Tom Jack
- Jone Lucy
- Jone Jack
- Lucy Mary
- Lucy Ben
- Jack Alice
- Jack Jesse
- Terry Alice
- Terry Jesse
- Philip Terry
- Philip Alma
- Mark Terry
- Mark Alma
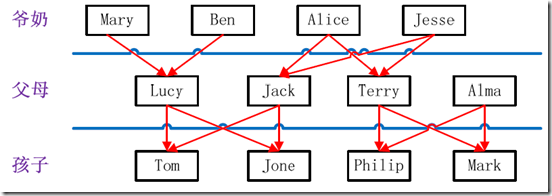
- 家族 树状关系谱:
家族谱
样例输出如下所示。
- file:grandchild grandparent
- Tom Alice
- Tom Jesse
- Jone Alice
- Jone Jesse
- Tom Mary
- Tom Ben
- Jone Mary
- Jone Ben
- Philip Alice
- Philip Jesse
- Mark Alice
- Mark Jesse
设计思路
分析这个实例,显然需要进行单表连接,连接的是 左表的 parent列和 右表的 child列,且 左表和 右表是 同一个表。
连接结果中 除去连接的两列就是所需要的结果——"grandchild--grandparent"表。要用MapReduce解决这个实例, 首先应该考虑如何实现 表的 自连接; 其次就是 连接列的 设置; 最后是 结果的 整理。
考虑到MapReduce的shuffle过程会将相同的key会连接在一起,所以可以将map结果的 key设置成 待连接的 列,然后列中相同的值就自然会连接在一起了。再与最开始的分析联系起来:
要连接的是左表的parent列和右表的child列,且左表和右表是同一个表,所以在 map阶段将 读入数据分割成 child和 parent之后,会将 parent设置成 key, child设置成 value进行输出,并作为 左表;再将 同一对child和 parent中的 child设置成 key, parent设置成 value进行输出,作为 右表。为了 区分输出中的 左右表,需要在输出的 value中 再加上 左右表的 信息,比如在value的String最开始处加上 字符1表示 左表,加上 字符2表示 右表。这样在map的结果中就形成了左表和右表,然后在shuffle过程中完成连接。reduce接收到连接的结果,其中每个key的value-list就包含了"grandchild--grandparent"关系。取出每个key的value-list进行解析,将 左表中的 child放入一个 数组, 右表中的 parent放入一个 数组,然后对 两个数组求笛卡尔积就是最后的结果了。
代码实现:
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.util.*;
- import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
- import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
- import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
- public class STjoin {
- public static int time = 0;
- /*
- * map将输出分割child和parent,然后正序输出一次作为右表,
- * 反序输出一次作为左表,需要注意的是在输出的value中必须
- * 加上左右表的区别标识。
- */
- public static class Map extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> {
- // 实现map函数
- public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
- throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- String childname = new String();// 孩子名称
- String parentname = new String();// 父母名称
- String relationtype = new String();// 左右表标识
- // 输入的一行预处理文本
- StringTokenizer itr=new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
- String[] values=new String[2];
- int i=0;
- while(itr.hasMoreTokens()){
- values[i]=itr.nextToken();
- i++;
- }
- if (values[0].compareTo("child") != 0) {
- childname = values[0];
- parentname = values[1];
- // 输出左表
- relationtype = "1";
- context.write(new Text(values[1]), new Text(relationtype +
- "+"+ childname + "+" + parentname));
- // 输出右表
- relationtype = "2";
- context.write(new Text(values[0]), new Text(relationtype +
- "+"+ childname + "+" + parentname));
- }
- }
- }
- public static class Reduce extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
- // 实现reduce函数
- public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
- throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- // 输出表头
- if (0 == time) {
- context.write(new Text("grandchild"), new Text("grandparent"));
- time++;
- }
- int grandchildnum = 0;
- String[] grandchild = new String[10];
- int grandparentnum = 0;
- String[] grandparent = new String[10];
- Iterator ite = values.iterator();
- while (ite.hasNext()) {
- String record = ite.next().toString();
- int len = record.length();
- int i = 2;
- if (0 == len) {
- continue;
- }
- // 取得左右表标识
- char relationtype = record.charAt(0);
- // 定义孩子和父母变量
- String childname = new String();
- String parentname = new String();
- // 获取value-list中value的child
- while (record.charAt(i) != '+') {
- childname += record.charAt(i);
- i++;
- }
- i = i + 1;
- // 获取value-list中value的parent
- while (i < len) {
- parentname += record.charAt(i);
- i++;
- }
- // 左表,取出child放入grandchildren
- if ('1' == relationtype) {
- grandchild[grandchildnum] = childname;
- grandchildnum++;
- }
- // 右表,取出parent放入grandparent
- if ('2' == relationtype) {
- grandparent[grandparentnum] = parentname;
- grandparentnum++;
- }
- }
- // grandchild和grandparent数组求笛卡尔儿积
- if (0 != grandchildnum && 0 != grandparentnum) {
- for (int m = 0; m < grandchildnum; m++) {
- for (int n = 0; n < grandparentnum; n++) {
- // 输出结果
- context.write(new Text(grandchild[m]), new Text(grandparent[n]));
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- Configuration conf = new Configuration();
- String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf,args).getRemainingArgs();
- if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
- System.err.println("Usage: Single Table Join <in> <out>");
- System.exit(2);
- }
- Job job = new Job(conf, "Single Table Join");
- job.setJarByClass(STjoin.class);
- // 设置Map和Reduce处理类
- job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
- job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
- // 设置输出类型
- job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
- job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
- // 设置输入和输出目录
- FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
- FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
- System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
- }
- }
二、多表关联
输入是两个文件,一个代表工厂表,包含工厂名列和地址编号列;另一个代表地址表,包含地址名列和地址编号列。要求从输入数据中找出工厂名和地址名的对应关系,输出"工厂名——地址名"表。
样例输入如下所示。
- 1)factory:
- factoryname addressed
- Beijing Red Star 1
- Shenzhen Thunder 3
- Guangzhou Honda 2
- Beijing Rising 1
- Guangzhou Development Bank 2
- Tencent 3
- Back of Beijing 1
- 2)address:
- addressID addressname
- 1 Beijing
- 2 Guangzhou
- 3 Shenzhen
- 4 Xian
- 样例输出如下所示。
- factoryname addressname
- Back of Beijing Beijing
- Beijing Red Star Beijing
- Beijing Rising Beijing
- Guangzhou Development Bank Guangzhou
- Guangzhou Honda Guangzhou
- Shenzhen Thunder Shenzhen
- Tencent Shenzhen
多表关联和单表关联相似,都类似于数据库中的自然连接。相比单表关联,多表关联的左右表和连接列更加清楚。所以可以采用和单表关联的相同的处理方式,map识别出输入的行属于哪个表之后,对其进行分割,将连接的列值保存在key中,另一列和左右表标识保存在value中,然后输出。reduce拿到连接结果之后,解析value内容,根据标志将左右表内容分开存放,然后求笛卡尔积,最后直接输出。
代码实现:
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.util.*;
- import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
- import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
- import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
- public class MTjoin {
- public static int time = 0;
- /*
- * 在map中先区分输入行属于左表还是右表,然后对两列值进行分割,
- * 保存连接列在key值,剩余列和左右表标志在value中,最后输出
- */
- public static class Map extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> {
- // 实现map函数
- public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
- throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- String line = value.toString();// 每行文件
- String relationtype = new String();// 左右表标识
- // 输入文件首行,不处理
- if (line.contains("factoryname") == true
- || line.contains("addressed") == true) {
- return;
- }
- // 输入的一行预处理文本
- StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(line);
- String mapkey = new String();
- String mapvalue = new String();
- int i = 0;
- while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
- // 先读取一个单词
- String token = itr.nextToken();
- // 判断该地址ID就把存到"values[0]"
- if (token.charAt(0) >= '0' && token.charAt(0) <= '9') {
- mapkey = token;
- if (i > 0) {
- relationtype = "1";
- } else {
- relationtype = "2";
- }
- continue;
- }
- // 存工厂名
- mapvalue += token + " ";
- i++;
- }
- // 输出左右表
- context.write(new Text(mapkey), new Text(relationtype + "+"+ mapvalue));
- }
- }
- /*
- * reduce解析map输出,将value中数据按照左右表分别保存,
- * 然后求出笛卡尔积,并输出。
- */
- public static class Reduce extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
- // 实现reduce函数
- public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
- throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- // 输出表头
- if (0 == time) {
- context.write(new Text("factoryname"), new Text("addressname"));
- time++;
- }
- int factorynum = 0;
- String[] factory = new String[10];
- int addressnum = 0;
- String[] address = new String[10];
- Iterator ite = values.iterator();
- while (ite.hasNext()) {
- String record = ite.next().toString();
- int len = record.length();
- int i = 2;
- if (0 == len) {
- continue;
- }
- // 取得左右表标识
- char relationtype = record.charAt(0);
- // 左表
- if ('1' == relationtype) {
- factory[factorynum] = record.substring(i);
- factorynum++;
- }
- // 右表
- if ('2' == relationtype) {
- address[addressnum] = record.substring(i);
- addressnum++;
- }
- }
- // 求笛卡尔积
- if (0 != factorynum && 0 != addressnum) {
- for (int m = 0; m < factorynum; m++) {
- for (int n = 0; n < addressnum; n++) {
- // 输出结果
- context.write(new Text(factory[m]),
- new Text(address[n]));
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- Configuration conf = new Configuration();
- String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
- if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
- System.err.println("Usage: Multiple Table Join <in> <out>");
- System.exit(2);
- }
- Job job = new Job(conf, "Multiple Table Join");
- job.setJarByClass(MTjoin.class);
- // 设置Map和Reduce处理类
- job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
- job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
- // 设置输出类型
- job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
- job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
- // 设置输入和输出目录
- FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
- FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
- System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
- }
- }